24 Jan 2024
Oxford Team Unveils Generative AI Models for Biomedical Analysis
Oxford’s CHI Lab Launches Accessible Generative AI for Biomedical Research
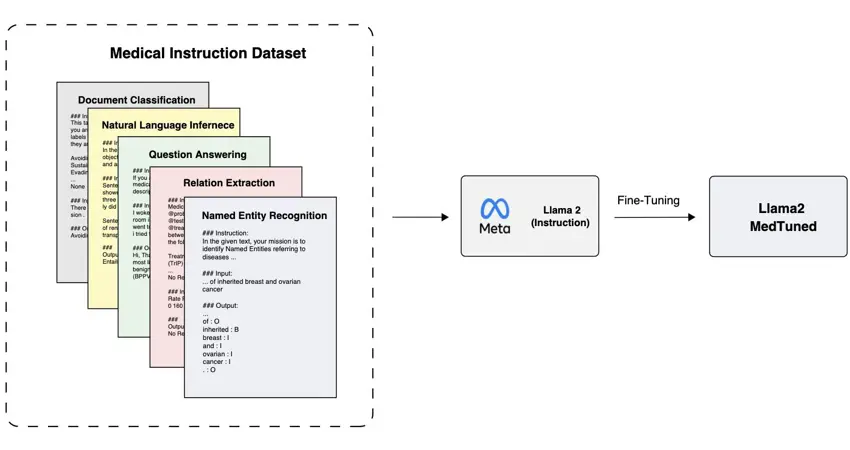
The Computational Health Informatics Lab at the University of Oxford, where Professor David A. Clifton leads a dynamic team including Senior Research Associate Dr. Omid Rohanian, has introduced cutting-edge generative AI models, Llama2-MedTuned-7b and Llama2-MedTuned-13b, aimed at refining biomedical and clinical language processing. These developments mark a substantial step forward in extending domain-specific “instruction-based” AI tools to a wider range of medical research and practice.
Understanding Generative AI Models
Generative AI models, capable of creating new content based on their training data, are transforming how medical information is processed. The Llama2-MedTuned models, trained on extensive medical texts, excel in tasks such as disease identification and extraction of crucial medical details from expansive datasets.
A Significant Resource for Healthcare and Research
Describing the benefits of these models, Dr Rohanian said "For healthcare professionals and researchers, who routinely navigate large volumes of biomedical literature, these models offer a significant advantage. They enhance the efficiency and accuracy of medical text analysis, supporting more informed diagnostics and patient record evaluation."
Commitment to Open Science
In line with the commitment to open science, the Oxford team has made these models and the associated dataset publicly available. This initiative allows for the global research community, especially those with limited computational resources, to utilise the power of generative AI in biomedical and clinical fields.
Advancing Biomedical AI
The introduction of Llama2-MedTuned-7b and Llama2-MedTuned-13b by the team at Oxford marks a pivotal step in the integration of AI within healthcare. It opens new pathways for research and enhances the capabilities of medical professionals in managing and utilising complex medical data.
Access the Models and Dataset Here:






