DINC: Distributed In-Network Computing - University of Oxford
Work by Changgang Zheng, Haoyue Tang, Mingyuan Zang, Xinpeng Hong, Aosong Feng, Leandros Tassiulas, and Noa Zilberman.
In-network computing provides significant performance benefits, load reduction, and power savings. Still, an in-network service’s functionality is strictly limited to a single hardware device. Research has focused on enabling on-device functionality, with limited consideration to distributed in-network computing. How to do distributed in-network computing on large network topology, realize full function on all paths, and coexist with normal network functions is a common challenge.
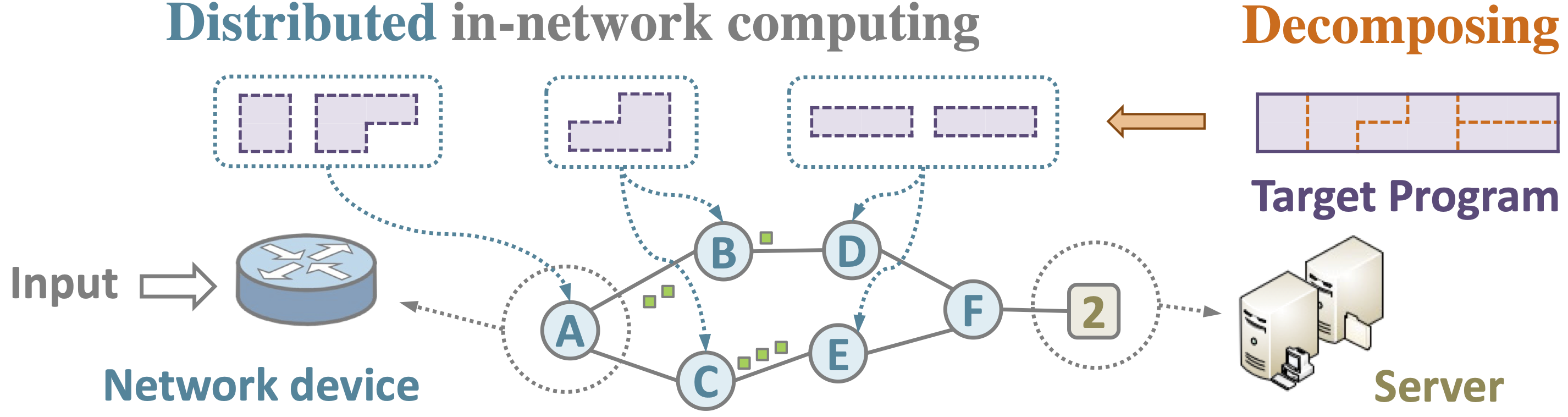
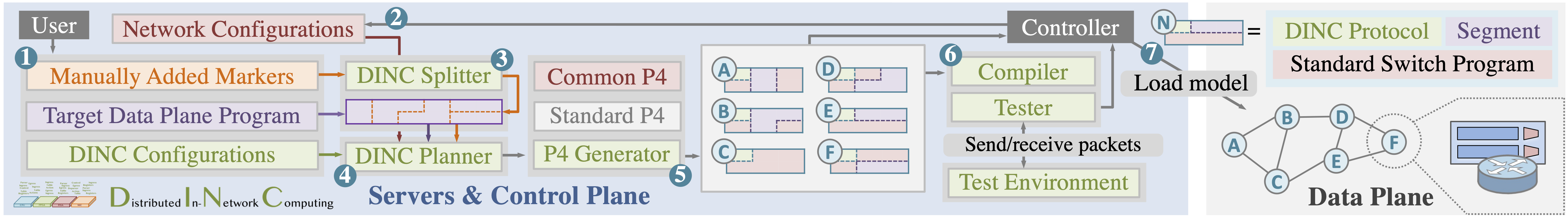
DINC is a framework that efficiently plans and implements P4-based service partitions on multiple network devices. DINC's planner supports any-to-any routing and is able to distribute and deploy program segments across network devices while providing full, correct functionality. To ensure co-existence with normal network functionality, DINC designs a code slicer and generator, extracting and generating P4 program slices following the planner's strategy.
DINC was evaluated using seven different workloads on both data center and wide-area network topologies (British Telecom network topology with more than 1000 nodes), demonstrating feasibility and scalability, and providing efficient distribution plans within seconds. It has been proved that DINC boosts applications' performance by utilizing network resources without compromising functionality.

