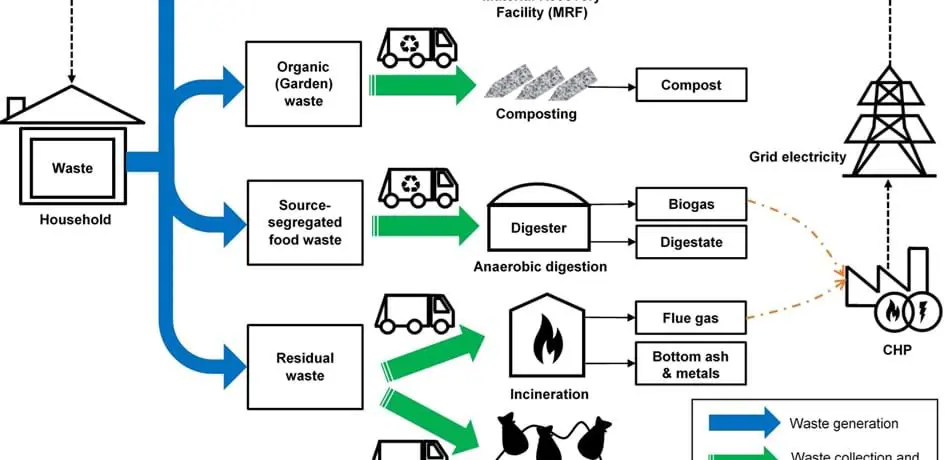
A sustainable waste management model for England is urgently needed to improve resource efficiency and divert waste from landfills. Dr Kok Siew Ng and Professor Aidong Yang have proposed a comprehensive system model to examine current waste management performance and project future waste generation, treatment and disposal scenarios in England.
Significant loss of valuable resources and increasing burdens on landfills are often associated with a lack of proper planning in waste management and resource recovery strategy. A sustainable waste management model is thus urgently needed to improve resource efficiency and divert more waste from landfills.
Dr Kok Siew Ng and Professor Aidong Yang have proposed a comprehensive system model to examine current waste management performance and project future waste generation, treatment and disposal scenarios in England.
The model comprises three integrated modules to represent household waste generation and collection; waste treatment and disposal; and energy recovery. A detailed mass and energy balance has been established and waste management performance has been evaluated using six upstream and downstream indicators. The base case scenario that assumes constant waste composition shows that waste to landfills can be reduced to less than 10% of the total amount, by 2035. However, it entails greater diversion of waste to energy-from-waste facilities, which is not sustainable and would incur higher capital investment and gate fees.
Alternative case scenarios that promote recycling instead of energy recovery result in lower capital investment and gate fees. Complete elimination of the food and organic fraction from the residual waste stream will help meet the 65% recycling target by 2035.
In light of the need for achieving a more circular economy in England, enhancing material recovery through reuse and recycling, reducing reliance on energy-from-waste and deploying more advanced waste valorisation technologies should be considered in future policy and planning for waste management.
Recommendations
The following recommendations are made for future waste management authorities to consider:
- Reducing future reliance on Energy-from-waste (EfW);
- Reconsidering the key metric to guide policy and practice;
- Advancing the management of food and organic waste; and
- Promoting circular economy through advanced resource recovery systems.
A paper entitled "Development of a system model to predict flows and performance of regional waste management planning: A case study of England" has been published in the Journal of Environmental Management.
The SYNERGORS Project
The SYNERGORS project (“A systems approach to synergistic utilisation of secondary organic streams”), funded by the Natural Environment Research Council (NERC), is led by Dr Kok Siew Ng. This project aims to develop new systems approaches and decision-making tools for promoting resource recovery from secondary organic waste streams including fossil- (e.g. used plastics) and biomass-derived waste (e.g. food waste, residual biomass).
Artificial intelligence and big data help rapid screening antibodies
Artificial Intelligence